External Recon Methodology
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE) Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
Check the subscription plans!
Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.

If you are interested in hacking career and hack the unhackable - we are hiring! (fluent polish written and spoken required).
Assets discoveries
So you were said that everything belonging to some company is inside the scope, and you want to figure out what this company actually owns.
The goal of this phase is to obtain all the companies owned by the main company and then all the assets of these companies. To do so, we are going to:
Find the acquisitions of the main company, this will give us the companies inside the scope.
Find the ASN (if any) of each company, this will give us the IP ranges owned by each company
Use reverse whois lookups to search for other entries (organisation names, domains...) related to the first one (this can be done recursively)
Use other techniques like shodan
organdsslfilters to search for other assets (thessltrick can be done recursively).
Acquisitions
First of all, we need to know which other companies are owned by the main company. One option is to visit https://www.crunchbase.com/, search for the main company, and click on "acquisitions". There you will see other companies acquired by the main one. Other option is to visit the Wikipedia page of the main company and search for acquisitions.
Ok, at this point you should know all the companies inside the scope. Lets figure out how to find their assets.
ASNs
An autonomous system number (ASN) is a unique number assigned to an autonomous system (AS) by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). An AS consists of blocks of IP addresses which have a distinctly defined policy for accessing external networks and are administered by a single organisation but may be made up of several operators.
It's interesting to find if the company have assigned any ASN to find its IP ranges. It will be interested to perform a vulnerability test against all the hosts inside the scope and look for domains inside these IPs. You can search by company name, by IP or by domain in https://bgp.he.net/. Depending on the region of the company this links could be useful to gather more data: AFRINIC (Africa), Arin(North America), APNIC (Asia), LACNIC (Latin America), RIPE NCC (Europe). Anyway, probably all the useful information (IP ranges and Whois) appears already in the first link.
Also, BBOT's subdomain enumeration automatically aggregates and summarizes ASNs at the end of the scan.
You can find the IP ranges of an organisation also using http://asnlookup.com/ (it has free API). You can find the IP and ASN of a domain using http://ipv4info.com/.
Looking for vulnerabilities
At this point we known all the assets inside the scope, so if you are allowed you could launch some vulnerability scanner (Nessus, OpenVAS) over all the hosts. Also, you could launch some port scans or use services like shodan to find open ports and depending on what you find you should take a look in this book to how to pentest several possible services running. Also, It could be worth it to mention that you can also prepare some default username and passwords lists and try to bruteforce services with https://github.com/x90skysn3k/brutespray.
Domains
We know all the companies inside the scope and their assets, it's time to find the domains inside the scope.
Please, note that in the following purposed techniques you can also find subdomains and that information shouldn't be underrated.
First of all you should look for the main domain(s) of each company. For example, for Tesla Inc. is going to be tesla.com.
Reverse DNS
As you have found all the IP ranges of the domains you could try to perform reverse dns lookups on those IPs to find more domains inside the scope. Try to use some dns server of the victim or some well-known dns server (1.1.1.1, 8.8.8.8)
For this to work, the administrator has to enable manually the PTR. You can also use a online tool for this info: http://ptrarchive.com/
Reverse Whois (loop)
Inside a whois you can find a lot of interesting information like organisation name, address, emails, phone numbers... But which is even more interesting is that you can find more assets related to the company if you perform reverse whois lookups by any of those fields (for example other whois registries where the same email appears). You can use online tools like:
https://www.reversewhois.io/ - Free
https://www.whoxy.com/ - Free web, not free API.
http://reversewhois.domaintools.com/ - Not free
https://drs.whoisxmlapi.com/reverse-whois-search - Not Free (only 100 free searches)
https://www.domainiq.com/ - Not Free
You can automate this task using DomLink (requires a whoxy API key).
You can also perform some automatic reverse whois discovery with amass: amass intel -d tesla.com -whois
Note that you can use this technique to discover more domain names every time you find a new domain.
Trackers
If find the same ID of the same tracker in 2 different pages you can suppose that both pages are managed by the same team. For example, if you see the same Google Analytics ID or the same Adsense ID on several pages.
There are some pages and tools that let you search by these trackers and more:
Favicon
Did you know that we can find related domains and sub domains to our target by looking for the same favicon icon hash? This is exactly what favihash.py tool made by @m4ll0k2 does. Here’s how to use it:
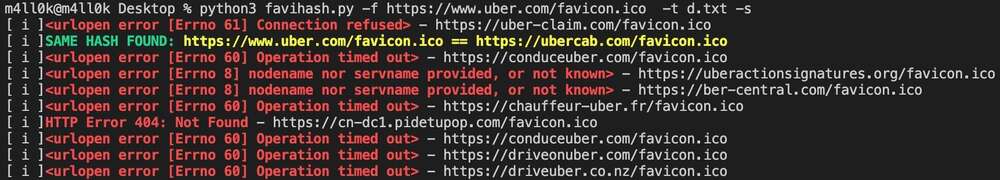
Simply said, favihash will allow us to discover domains that have the same favicon icon hash as our target.
Moreover, you can also search technologies using the favicon hash as explained in this blog post. That means that if you know the hash of the favicon of a vulnerable version of a web tech you can search if in shodan and find more vulnerable places:
This is how you can calculate the favicon hash of a web:
Copyright / Uniq string
Search inside the web pages strings that could be shared across different webs in the same organisation. The copyright string could be a good example. Then search for that string in google, in other browsers or even in shodan: shodan search http.html:"Copyright string"
CRT Time
It's common to have a cron job such as
to renew the all the domain certificates on the server. This means that even if the CA used for this doesn't set the time it was generated in the Validity time, it's possible to find domains belonging to the same company in the certificate transparency logs. Check out this writeup for more information.
Mail DMARC information
You can use a web such as https://dmarc.live/info/google.com or a tool such as https://github.com/Tedixx/dmarc-subdomains to find domains and subdomain sharing the same dmarc information.
Passive Takeover
Apparently is common for people to assign subdomains to IPs that belongs to cloud providers and at some point lose that IP address but forget about removing the DNS record. Therefore, just spawning a VM in a cloud (like Digital Ocean) you will be actually taking over some subdomains(s).
This post explains a store about it and propose a script that spawns a VM in DigitalOcean, gets the IPv4 of the new machine, and searches in Virustotal for subdomain records pointing to it.
Other ways
Note that you can use this technique to discover more domain names every time you find a new domain.
Shodan
As you already know the name of the organisation owning the IP space. You can search by that data in shodan using: org:"Tesla, Inc." Check the found hosts for new unexpected domains in the TLS certificate.
You could access the TLS certificate of the main web page, obtain the Organisation name and then search for that name inside the TLS certificates of all the web pages known by shodan with the filter : ssl:"Tesla Motors" or use a tool like sslsearch.
Assetfinder
Assetfinder is a tool that look for domains related with a main domain and subdomains of them, pretty amazing.
Looking for vulnerabilities
Check for some domain takeover. Maybe some company is using some a domain but they lost the ownership. Just register it (if cheap enough) and let know the company.
If you find any domain with an IP different from the ones you already found in the assets discovery, you should perform a basic vulnerability scan (using Nessus or OpenVAS) and some port scan with nmap/masscan/shodan. Depending on which services are running you can find in this book some tricks to "attack" them. Note that sometimes the domain is hosted inside an IP that is not controlled by the client, so it's not in the scope, be careful.
 Bug bounty tip: sign up for Intigriti, a premium bug bounty platform created by hackers, for hackers! Join us at https://go.intigriti.com/hacktricks today, and start earning bounties up to $100,000!
Bug bounty tip: sign up for Intigriti, a premium bug bounty platform created by hackers, for hackers! Join us at https://go.intigriti.com/hacktricks today, and start earning bounties up to $100,000!
Subdomains
We know all the companies inside the scope, all the assets of each company and all the domains related to the companies.
It's time to find all the possible subdomains of each found domain.
Note that some of the tools and techniques to find domains can also help to find subdomains!
DNS
Let's try to get subdomains from the DNS records. We should also try for Zone Transfer (If vulnerable, you should report it).
OSINT
The fastest way to obtain a lot of subdomains is search in external sources. The most used tools are the following ones (for better results configure the API keys):
There are other interesting tools/APIs that even if not directly specialised in finding subdomains could be useful to find subdomains, like:
Crobat: Uses the API https://sonar.omnisint.io to obtain subdomains
RapidDNS free API
gau: fetches known URLs from AlienVault's Open Threat Exchange, the Wayback Machine, and Common Crawl for any given domain.
SubDomainizer & subscraper: They scrap the web looking for JS files and extract subdomains from there.
securitytrails.com has a free API to search for subdomains and IP history
This project offers for free all the subdomains related to bug-bounty programs. You can access this data also using chaospy or even access the scope used by this project https://github.com/projectdiscovery/chaos-public-program-list
You can find a comparison of many of these tools here: https://blog.blacklanternsecurity.com/p/subdomain-enumeration-tool-face-off
DNS Brute force
Let's try to find new subdomains brute-forcing DNS servers using possible subdomain names.
For this action you will need some common subdomains wordlists like:
And also IPs of good DNS resolvers. In order to generate a list of trusted DNS resolvers you can download the resolvers from https://public-dns.info/nameservers-all.txt and use dnsvalidator to filter them. Or you could use: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/trickest/resolvers/main/resolvers-trusted.txt
The most recommended tools for DNS brute-force are:
massdns: This was the first tool that performed an effective DNS brute-force. It's very fast however it's prone to false positives.
gobuster: This one I think just uses 1 resolver
shuffledns is a wrapper around
massdns, written in go, that allows you to enumerate valid subdomains using active bruteforce, as well as resolve subdomains with wildcard handling and easy input-output support.
puredns: It also uses
massdns.
aiodnsbrute uses asyncio to brute force domain names asynchronously.
Second DNS Brute-Force Round
After having found subdomains using open sources and brute-forcing, you could generate alterations of the subdomains found to try to find even more. Several tools are useful for this purpose:
dnsgen: Given the domains and subdomains generate permutations.
gotator: Given the domains and subdomains generate permutations. If not permutations file is indicated gotator will use its own one.
alterx: Based on a domain it generates new potential subdomains names based on indicated patterns to try to discover more subdomains.
Smart permutations generation
subzuf: subzuf is a subdomain brute-force fuzzer coupled with an immensly simple but effective DNS reponse-guided algorithm. It utilizes a provided set of input data, like a tailored wordlist or historical DNS/TLS records, to accurately synthesize more corresponding domain names and expand them even further in a loop based on information gathered during DNS scan.
Subdomain Discovery Workflow
Check this blog post I wrote about how to automate the subdomain discovery from a domain using Trickest workflows so I don't need to launch manually a bunch of tools in my computer:
VHosts / Virtual Hosts
If you found an IP address containing one or several web pages belonging to subdomains, you could try to find other subdomains with webs in that IP by looking in OSINT sources for domains in an IP or by brute-forcing VHost domain names in that IP.
OSINT
You can find some VHosts in IPs using HostHunter or other APIs.
Brute Force
If you suspect that some subdomain can be hidden in a web server you could try to brute force it:
With this technique you may even be able to access internal/hidden endpoints.
CORS Brute Force
Sometimes you will find pages that only return the header Access-Control-Allow-Origin when a valid domain/subdomain is set in the Origin header. In these scenarios, you can abuse this behaviour to discover new subdomains.
Buckets Brute Force
While looking for subdomains keep an eye to see if it is pointing to any type of bucket, and in that case check the permissions. Also, as at this point you will know all the domains inside the scope, try to brute force possible bucket names and check the permissions.
Monitorization
You can monitor if new subdomains of a domain are created by monitoring the Certificate Transparency Logs sublert does.
Looking for vulnerabilities
Check for possible subdomain takeovers. If the subdomain is pointing to some S3 bucket, check the permissions.
If you find any subdomain with an IP different from the ones you already found in the assets discovery, you should perform a basic vulnerability scan (using Nessus or OpenVAS) and some port scan with nmap/masscan/shodan. Depending on which services are running you can find in this book some tricks to "attack" them. Note that sometimes the subdomain is hosted inside an IP that is not controlled by the client, so it's not in the scope, be careful.
IPs
In the initial steps you might have found some IP ranges, domains and subdomains. It’s time to recollect all the IPs from those ranges and for the domains/subdomains (DNS queries).
Using services from the following free apis you can also find previous IPs used by domains and subdomains. These IPs might still be owned by the client (and might allow you to find CloudFlare bypasses)
You can also check for domains pointing a specific IP address using the tool hakip2host
Looking for vulnerabilities
Port scan all the IPs that doesn’t belong to CDNs (as you highly probably won’t find anything interested in there). In the running services discovered you might be able to find vulnerabilities.
Find a guide about how to scan hosts.
Web servers hunting
We have found all the companies and their assets and we know IP ranges, domains and subdomains inside the scope. It's time to search for web servers.
In the previous steps you have probably already performed some recon of the IPs and domains discovered, so you may have already found all the possible web servers. However, if you haven't we are now going to see some fast tricks to search for web servers inside the scope.
Please, note that this will be oriented for web apps discovery, so you should perform the vulnerability and port scanning also (if allowed by the scope).
A fast method to discover ports open related to web servers using masscan can be found here. Another friendly tool to look for web servers is httprobe, fprobe and httpx. You just pass a list of domains and it will try to connect to port 80 (http) and 443 (https). Additionally, you can indicate to try other ports:
Screenshots
Now that you have discovered all the web servers present in the scope (among the IPs of the company and all the domains and subdomains) you probably don't know where to start. So, let's make it simple and start just taking screenshots of all of them. Just by taking a look at the main page you can find weird endpoints that are more prone to be vulnerable.
To perform the proposed idea you can use EyeWitness, HttpScreenshot, Aquatone, Shutter, Gowitness or webscreenshot.
Moreover, you could then use eyeballer to run over all the screenshots to tell you what's likely to contain vulnerabilities, and what isn't.
Public Cloud Assets
In order to find potential cloud assets belonging to a company you should start with a list of keywords that identify that company. For example, a crypto for a crypto company you might use words such as: "crypto", "wallet", "dao", "<domain_name>", <"subdomain_names">.
You will also need wordlists of common words used in buckets:
Then, with those words you should generate permutations (check the Second Round DNS Brute-Force for more info).
With the resulting wordlists you could use tools such as cloud_enum, CloudScraper, cloudlist or S3Scanner.
Remember that when looking for Cloud Assets you should look for more than just buckets in AWS.
Looking for vulnerabilities
If you find things such as open buckets or cloud functions exposed you should access them and try to see what they offer you and if you can abuse them.
Emails
With the domains and subdomains inside the scope you basically have all what you need to start searching for emails. These are the APIs and tools that have worked the best for me to find emails of a company:
theHarvester - with APIs
API of https://hunter.io/ (free version)
API of https://app.snov.io/ (free version)
API of https://minelead.io/ (free version)
Looking for vulnerabilities
Emails will come handy later to brute-force web logins and auth services (such as SSH). Also, they are needed for phishings. Moreover, these APIs will give you even more info about the person behind the email, which is useful for the phishing campaign.
Credential Leaks
With the domains, subdomains, and emails you can start looking for credentials leaked in the past belonging to those emails:
Looking for vulnerabilities
If you find valid leaked credentials, this is a very easy win.
Secrets Leaks
Credential leaks are related to hacks of companies where sensitive information was leaked and sold. However, companies might be affected for other leaks whose info isn't in those databases:
Github Leaks
Credentials and APIs might be leaked in the public repositories of the company or of the users working by that github company. You can use the tool Leakos to download all the public repos of an organization and of its developers and run gitleaks over them automatically.
Leakos can also be used to run gitleaks agains all the text provided URLs passed to it as sometimes web pages also contains secrets.
Github Dorks
Check also this page for potential github dorks you could also search for in the organization you are attacking:
Github Dorks & LeaksPastes Leaks
Sometimes attackers or just workers will publish company content in a paste site. This might or might not contain sensitive information, but it's very interesting to search for it. You can use the tool Pastos to search in more that 80 paste sites at the same time.
Google Dorks
Old but gold google dorks are always useful to find exposed information that shouldn't be there. The only problem is that the google-hacking-database contains several thousands of possible queries that you cannot run manually. So, you can get your favourite 10 ones or you could use a tool such as Gorks to run them all.
Note that the tools that expect to run all the database using the regular Google browser will never end as google will block you very very soon.
Looking for vulnerabilities
If you find valid leaked credentials or API tokens, this is a very easy win.
Public Code Vulnerabilities
If you found that the company has open-source code you can analyse it and search for vulnerabilities on it.
Depending on the language there are different tools you can use:
Source code Review / SAST ToolsThere are also free services that allow you to scan public repositories, such as:
The majority of the vulnerabilities found by bug hunters resides inside web applications, so at this point I would like to talk about a web application testing methodology, and you can find this information here.
I also want to do a special mention to the section Web Automated Scanners open source tools, as, if you shouldn't expect them to find you very sensitive vulnerabilities, they come handy to implement them on workflows to have some initial web information.
Recapitulation
Congratulations! At this point you have already perform all the basic enumeration. Yes, it's basic because a lot more enumeration can be done (will see more tricks later).
So you have already:
Found all the companies inside the scope
Found all the assets belonging to the companies (and perform some vuln scan if in scope)
Found all the domains belonging to the companies
Found all the subdomains of the domains (any subdomain takeover?)
Found all the IPs (from and not from CDNs) inside the scope.
Found all the web servers and took a screenshot of them (anything weird worth a deeper look?)
Found all the potential public cloud assets belonging to the company.
Emails, credentials leaks, and secret leaks that could give you a big win very easily.
Pentesting all the webs you found
Full Recon Automatic Tools
There are several tools out there that will perform part of the proposed actions against a given scope.
https://github.com/hackerspider1/EchoPwn - A little old and not updated
References
All free courses of @Jhaddix like The Bug Hunter's Methodology v4.0 - Recon Edition

If you are interested in hacking career and hack the unhackable - we are hiring! (fluent polish written and spoken required).
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE) Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
Check the subscription plans!
Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Last updated
