Windows Artifacts
Windows Artifacts
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE) Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
Check the subscription plans!
Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Generic Windows Artifacts
Windows 10 Notifications
In the path \Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Notifications you can find the database appdb.dat (before Windows anniversary) or wpndatabase.db (after Windows Anniversary).
Inside this SQLite database, you can find the Notification table with all the notifications (in XML format) that may contain interesting data.
Timeline
Timeline is a Windows characteristic that provides chronological history of web pages visited, edited documents, and executed applications.
The database resides in the path \Users\<username>\AppData\Local\ConnectedDevicesPlatform\<id>\ActivitiesCache.db. This database can be opened with an SQLite tool or with the tool WxTCmd which generates 2 files that can be opened with the tool TimeLine Explorer.
ADS (Alternate Data Streams)
Files downloaded may contain the ADS Zone.Identifier indicating how it was downloaded from the intranet, internet, etc. Some software (like browsers) usually put even more information like the URL from where the file was downloaded.
File Backups
Recycle Bin
In Vista/Win7/Win8/Win10 the Recycle Bin can be found in the folder $Recycle.bin in the root of the drive (C:\$Recycle.bin).
When a file is deleted in this folder 2 specific files are created:
$I{id}: File information (date of when it was deleted}$R{id}: Content of the file

Having these files you can use the tool Rifiuti to get the original address of the deleted files and the date it was deleted (use rifiuti-vista.exe for Vista – Win10).

Volume Shadow Copies
Shadow Copy is a technology included in Microsoft Windows that can create backup copies or snapshots of computer files or volumes, even when they are in use.
These backups are usually located in the \System Volume Information from the root of the file system and the name is composed of UIDs shown in the following image:

Mounting the forensics image with the ArsenalImageMounter, the tool ShadowCopyView can be used to inspect a shadow copy and even extract the files from the shadow copy backups.

The registry entry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\BackupRestore contains the files and keys to not backup:

The registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\VSS also contains configuration information about the Volume Shadow Copies.
Office AutoSaved Files
You can find the office autosaved files in: C:\Usuarios\\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft{Excel|Word|Powerpoint}\
Shell Items
A shell item is an item that contains information about how to access another file.
Recent Documents (LNK)
Windows automatically creates these shortcuts when the user open, uses or creates a file in:
Win7-Win10:
C:\Users\\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Recent\Office:
C:\Users\\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Office\Recent\
When a folder is created, a link to the folder, to the parent folder, and the grandparent folder is also created.
These automatically created link files contain information about the origin like if it's a file or a folder, MAC times of that file, volume information of where is the file stored and folder of the target file. This information can be useful to recover those files in case they were removed.
Also, the date created of the link file is the first time the original file was first used and the date modified of the link file is the last time the origin file was used.
To inspect these files you can use LinkParser.
In this tools you will find 2 sets of timestamps:
First Set:
FileModifiedDate
FileAccessDate
FileCreationDate
Second Set:
LinkModifiedDate
LinkAccessDate
LinkCreationDate.
The first set of timestamp references the timestamps of the file itself. The second set references the timestamps of the linked file.
You can get the same information running the Windows CLI tool: LECmd.exe
In this case, the information is going to be saved inside a CSV file.
Jumplists
These are the recent files that are indicated per application. It's the list of recent files used by an application that you can access on each application. They can be created automatically or be custom.
The jumplists created automatically are stored in C:\Users\{username}\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Recent\AutomaticDestinations\. The jumplists are named following the format {id}.autmaticDestinations-ms where the initial ID is the ID of the application.
The custom jumplists are stored in C:\Users\{username}\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Recent\CustomDestination\ and they are created by the application usually because something important has happened with the file (maybe marked as favorite)
The created time of any jumplist indicates the the first time the file was accessed and the modified time the last time.
You can inspect the jumplists using JumplistExplorer.

(Note that the timestamps provided by JumplistExplorer are related to the jumplist file itself)
Shellbags
Follow this link to learn what are the shellbags.
Use of Windows USBs
It's possible to identify that a USB device was used thanks to the creation of:
Windows Recent Folder
Microsoft Office Recent Folder
Jumplists
Note that some LNK file instead of pointing to the original path, points to the WPDNSE folder:

The files in the folder WPDNSE are a copy of the original ones, then won't survive a restart of the PC and the GUID is taken from a shellbag.
Registry Information
Check this page to learn which registry keys contain interesting information about USB connected devices.
setupapi
Check the file C:\Windows\inf\setupapi.dev.log to get the timestamps about when the USB connection was produced (search for Section start).

USB Detective
USBDetective can be used to obtain information about the USB devices that have been connected to an image.
Plug and Play Cleanup
The scheduled task known as 'Plug and Play Cleanup' is primarily designed for the removal of outdated driver versions. Contrary to its specified purpose of retaining the latest driver package version, online sources suggest it also targets drivers that have been inactive for 30 days. Consequently, drivers for removable devices not connected in the past 30 days may be subject to deletion.
The task is located at the following path: C:\Windows\System32\Tasks\Microsoft\Windows\Plug and Play\Plug and Play Cleanup.
A screenshot depicting the task's content is provided: 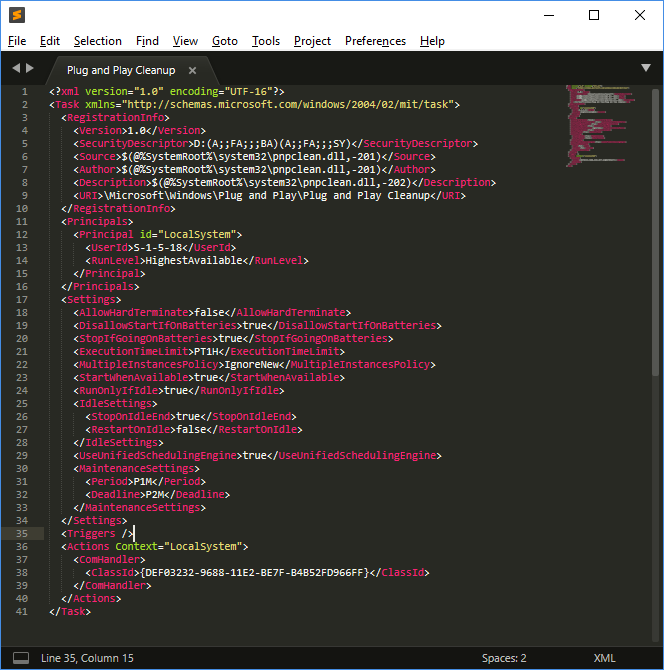
Key Components and Settings of the Task:
pnpclean.dll: This DLL is responsible for the actual cleanup process.
UseUnifiedSchedulingEngine: Set to
TRUE, indicating the use of the generic task scheduling engine.MaintenanceSettings:
Period ('P1M'): Directs the Task Scheduler to initiate the cleanup task monthly during regular Automatic maintenance.
Deadline ('P2M'): Instructs the Task Scheduler, if the task fails for two consecutive months, to execute the task during emergency Automatic maintenance.
This configuration ensures regular maintenance and cleanup of drivers, with provisions for reattempting the task in case of consecutive failures.
For more information check: https://blog.1234n6.com/2018/07/windows-plug-and-play-cleanup.html
Emails
Emails contain 2 interesting parts: The headers and the content of the email. In the headers you can find information like:
Who sent the emails (email address, IP, mail servers that have redirected the email)
When was the email sent
Also, inside the References and In-Reply-To headers you can find the ID of the messages:

Windows Mail App
This application saves emails in HTML or text. You can find the emails inside subfolders inside \Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Comms\Unistore\data\3\. The emails are saved with the .dat extension.
The metadata of the emails and the contacts can be found inside the EDB database: \Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Comms\UnistoreDB\store.vol
Change the extension of the file from .vol to .edb and you can use the tool ESEDatabaseView to open it. Inside the Message table you can see the emails.
Microsoft Outlook
When Exchange servers or Outlook clients are used there are going to be some MAPI headers:
Mapi-Client-Submit-Time: Time of the system when the email was sentMapi-Conversation-Index: Number of children messages of the thread and timestamp of each message of the threadMapi-Entry-ID: Message identifier.Mappi-Message-FlagsandPr_last_Verb-Executed: Information about the MAPI client (message read? no read? responded? redirected? out of the office?)
In the Microsoft Outlook client, all the sent/received messages, contacts data, and calendar data are stored in a PST file in:
%USERPROFILE%\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Outlook(WinXP)%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outlook
The registry path HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Windows Messaging Subsystem\Profiles\Outlook indicates the file that is being used.
You can open the PST file using the tool Kernel PST Viewer.

Microsoft Outlook OST Files
An OST file is generated by Microsoft Outlook when it's configured with IMAP or an Exchange server, storing similar information to a PST file. This file is synchronized with the server, retaining data for the last 12 months up to a maximum size of 50GB, and is located in the same directory as the PST file. To view an OST file, the Kernel OST viewer can be utilized.
Retrieving Attachments
Lost attachments might be recoverable from:
For IE10:
%APPDATA%\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet Files\Content.OutlookFor IE11 and above:
%APPDATA%\Local\Microsoft\InetCache\Content.Outlook
Thunderbird MBOX Files
Thunderbird utilizes MBOX files to store data, located at \Users\%USERNAME%\AppData\Roaming\Thunderbird\Profiles.
Image Thumbnails
Windows XP and 8-8.1: Accessing a folder with thumbnails generates a
thumbs.dbfile storing image previews, even after deletion.Windows 7/10:
thumbs.dbis created when accessed over a network via UNC path.Windows Vista and newer: Thumbnail previews are centralized in
%userprofile%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Explorerwith files named thumbcache_xxx.db. Thumbsviewer and ThumbCache Viewer are tools for viewing these files.
Windows Registry Information
The Windows Registry, storing extensive system and user activity data, is contained within files in:
%windir%\System32\Configfor variousHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEsubkeys.%UserProfile%{User}\NTUSER.DATforHKEY_CURRENT_USER.Windows Vista and later versions back up
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEregistry files in%Windir%\System32\Config\RegBack\.Additionally, program execution information is stored in
%UserProfile%\{User}\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\USERCLASS.DATfrom Windows Vista and Windows 2008 Server onwards.
Tools
Some tools are useful to analyze the registry files:
Registry Editor: It's installed in Windows. It's a GUI to navigate through the Windows registry of the current session.
Registry Explorer: It allows you to load the registry file and navigate through them with a GUI. It also contains Bookmarks highlighting keys with interesting information.
RegRipper: Again, it has a GUI that allows to navigate through the loaded registry and also contains plugins that highlight interesting information inside the loaded registry.
Windows Registry Recovery: Another GUI application capable of extracting the important information from the registry loaded.
Recovering Deleted Element
When a key is deleted it's marked as such, but until the space it's occupying is needed it won't be removed. Therefore, using tools like Registry Explorer it's possible to recover these deleted keys.
Last Write Time
Each Key-Value contains a timestamp indicating the last time it was modified.
SAM
The file/hive SAM contains the users, groups and users passwords hashes of the system.
In SAM\Domains\Account\Users you can obtain the username, the RID, last login, last failed logon, login counter, password policy and when the account was created. To get the hashes you also need the file/hive SYSTEM.
Interesting entries in the Windows Registry
Interesting Windows Registry KeysPrograms Executed
Basic Windows Processes
In this post you can learn about the common Windows processes to detect suspicious behaviours.
Windows Recent APPs
Inside the registry NTUSER.DAT in the path Software\Microsoft\Current Version\Search\RecentApps you can subkeys with information about the application executed, last time it was executed, and number of times it was launched.
BAM (Background Activity Moderator)
You can open the SYSTEM file with a registry editor and inside the path SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\bam\UserSettings\{SID} you can find the information about the applications executed by each user (note the {SID} in the path) and at what time they were executed (the time is inside the Data value of the registry).
Windows Prefetch
Prefetching is a technique that allows a computer to silently fetch the necessary resources needed to display content that a user might access in the near future so resources can be accessed quicker.
Windows prefetch consists of creating caches of the executed programs to be able to load them faster. These caches as created as .pf files inside the path: C:\Windows\Prefetch. There is a limit of 128 files in XP/VISTA/WIN7 and 1024 files in Win8/Win10.
The file name is created as {program_name}-{hash}.pf (the hash is based on the path and arguments of the executable). In W10 these files are compressed. Do note that the sole presence of the file indicates that the program was executed at some point.
The file C:\Windows\Prefetch\Layout.ini contains the names of the folders of the files that are prefetched. This file contains information about the number of the executions, dates of the execution and files open by the program.
To inspect these files you can use the tool PEcmd.exe:

Superprefetch
Superprefetch has the same goal as prefetch, load programs faster by predicting what is going to be loaded next. However, it doesn't substitute the prefetch service.
This service will generate database files in C:\Windows\Prefetch\Ag*.db.
In these databases you can find the name of the program, number of executions, files opened, volume accessed, complete path, timeframes and timestamps.
You can access this information using the tool CrowdResponse.
SRUM
System Resource Usage Monitor (SRUM) monitors the resources consumed by a process. It appeared in W8 and it stores the data in an ESE database located in C:\Windows\System32\sru\SRUDB.dat.
It gives the following information:
AppID and Path
User that executed the process
Sent Bytes
Received Bytes
Network Interface
Connection duration
Process duration
This information is updated every 60 mins.
You can obtain the date from this file using the tool srum_dump.
AppCompatCache (ShimCache)
The AppCompatCache, also known as ShimCache, forms a part of the Application Compatibility Database developed by Microsoft to tackle application compatibility issues. This system component records various pieces of file metadata, which include:
Full path of the file
Size of the file
Last Modified time under $Standard_Information (SI)
Last Updated time of the ShimCache
Process Execution Flag
Such data is stored within the registry at specific locations based on the version of the operating system:
For XP, the data is stored under
SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\Appcompatibility\AppcompatCachewith a capacity for 96 entries.For Server 2003, as well as for Windows versions 2008, 2012, 2016, 7, 8, and 10, the storage path is
SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\AppcompatCache\AppCompatCache, accommodating 512 and 1024 entries, respectively.
To parse the stored information, the AppCompatCacheParser tool is recommended for use.

Amcache
The Amcache.hve file is essentially a registry hive that logs details about applications that have been executed on a system. It is typically found at C:\Windows\AppCompat\Programas\Amcache.hve.
This file is notable for storing records of recently executed processes, including the paths to the executable files and their SHA1 hashes. This information is invaluable for tracking the activity of applications on a system.
To extract and analyze the data from Amcache.hve, the AmcacheParser tool can be used. The following command is an example of how to use AmcacheParser to parse the contents of the Amcache.hve file and output the results in CSV format:
Among the generated CSV files, the Amcache_Unassociated file entries is particularly noteworthy due to the rich information it provides about unassociated file entries.
The most interesting CVS file generated is the Amcache_Unassociated file entries.
RecentFileCache
This artifact can only be found in W7 in C:\Windows\AppCompat\Programs\RecentFileCache.bcf and it contains information about the recent execution of some binaries.
You can use the tool RecentFileCacheParse to parse the file.
Scheduled tasks
You can extract them from C:\Windows\Tasks or C:\Windows\System32\Tasks and read them as XML.
Services
You can find them in the registry under SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services. You can see what is going to be executed and when.
Windows Store
The installed applications can be found in \ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\AppRepository\
This repository has a log with each application installed in the system inside the database StateRepository-Machine.srd.
Inside the Application table of this database, it's possible to find the columns: "Application ID", "PackageNumber", and "Display Name". These columns have information about pre-installed and installed applications and it can be found if some applications were uninstalled because the IDs of installed applications should be sequential.
It's also possible to find installed application inside the registry path: Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Appx\AppxAllUserStore\Applications\
And uninstalled applications in: Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Appx\AppxAllUserStore\Deleted\
Windows Events
Information that appears inside Windows events are:
What happened
Timestamp (UTC + 0)
Users involved
Hosts involved (hostname, IP)
Assets accessed (files, folder, printer, services)
The logs are located in C:\Windows\System32\config before Windows Vista and in C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs after Windows Vista. Before Windows Vista, the event logs were in binary format and after it, they are in XML format and use the .evtx extension.
The location of the event files can be found in the SYSTEM registry in HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\EventLog\{Application|System|Security}
They can be visualized from the Windows Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc) or with other tools like Event Log Explorer or Evtx Explorer/EvtxECmd.
Understanding Windows Security Event Logging
Access events are recorded in the security configuration file located at C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Security.evtx. This file's size is adjustable, and when its capacity is reached, older events are overwritten. Recorded events include user logins and logoffs, user actions, and changes to security settings, as well as file, folder, and shared asset access.
Key Event IDs for User Authentication:
EventID 4624: Indicates a user successfully authenticated.
EventID 4625: Signals an authentication failure.
EventIDs 4634/4647: Represent user logoff events.
EventID 4672: Denotes login with administrative privileges.
Sub-types within EventID 4634/4647:
Interactive (2): Direct user login.
Network (3): Access to shared folders.
Batch (4): Execution of batch processes.
Service (5): Service launches.
Proxy (6): Proxy authentication.
Unlock (7): Screen unlocked with a password.
Network Cleartext (8): Clear text password transmission, often from IIS.
New Credentials (9): Usage of different credentials for access.
Remote Interactive (10): Remote desktop or terminal services login.
Cache Interactive (11): Login with cached credentials without domain controller contact.
Cache Remote Interactive (12): Remote login with cached credentials.
Cached Unlock (13): Unlocking with cached credentials.
Status and Sub Status Codes for EventID 4625:
0xC0000064: User name does not exist - Could indicate a username enumeration attack.
0xC000006A: Correct user name but wrong password - Possible password guessing or brute-force attempt.
0xC0000234: User account locked out - May follow a brute-force attack resulting in multiple failed logins.
0xC0000072: Account disabled - Unauthorized attempts to access disabled accounts.
0xC000006F: Logon outside allowed time - Indicates attempts to access outside of set login hours, a possible sign of unauthorized access.
0xC0000070: Violation of workstation restrictions - Could be an attempt to login from an unauthorized location.
0xC0000193: Account expiration - Access attempts with expired user accounts.
0xC0000071: Expired password - Login attempts with outdated passwords.
0xC0000133: Time sync issues - Large time discrepancies between client and server may be indicative of more sophisticated attacks like pass-the-ticket.
0xC0000224: Mandatory password change required - Frequent mandatory changes might suggest an attempt to destabilize account security.
0xC0000225: Indicates a system bug rather than a security issue.
0xC000015b: Denied logon type - Access attempt with unauthorized logon type, such as a user trying to execute a service logon.
EventID 4616:
Time Change: Modification of the system time, could obscure the timeline of events.
EventID 6005 and 6006:
System Startup and Shutdown: EventID 6005 indicates the system starting up, while EventID 6006 marks it shutting down.
EventID 1102:
Log Deletion: Security logs being cleared, which is often a red flag for covering up illicit activities.
EventIDs for USB Device Tracking:
20001 / 20003 / 10000: USB device first connection.
10100: USB driver update.
EventID 112: Time of USB device insertion.
For practical examples on simulating these login types and credential dumping opportunities, refer to Altered Security's detailed guide.
Event details, including status and sub-status codes, provide further insights into event causes, particularly notable in Event ID 4625.
Recovering Windows Events
To enhance the chances of recovering deleted Windows Events, it's advisable to power down the suspect computer by directly unplugging it. Bulk_extractor, a recovery tool specifying the .evtx extension, is recommended for attempting to recover such events.
Identifying Common Attacks via Windows Events
For a comprehensive guide on utilizing Windows Event IDs in identifying common cyber attacks, visit Red Team Recipe.
Brute Force Attacks
Identifiable by multiple EventID 4625 records, followed by an EventID 4624 if the attack succeeds.
Time Change
Recorded by EventID 4616, changes to system time can complicate forensic analysis.
USB Device Tracking
Useful System EventIDs for USB device tracking include 20001/20003/10000 for initial use, 10100 for driver updates, and EventID 112 from DeviceSetupManager for insertion timestamps.
System Power Events
EventID 6005 indicates system startup, while EventID 6006 marks shutdown.
Log Deletion
Security EventID 1102 signals the deletion of logs, a critical event for forensic analysis.
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE) Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
Check the subscription plans!
Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Last updated