ACLs - DACLs/SACLs/ACEs

Use Trickest to easily build and automate workflows powered by the world's most advanced community tools. Get Access Today:
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE) Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
Check the subscription plans!
Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Access Control List (ACL)
An Access Control List (ACL) consists of an ordered set of Access Control Entries (ACEs) that dictate the protections for an object and its properties. In essence, an ACL defines which actions by which security principals (users or groups) are permitted or denied on a given object.
There are two types of ACLs:
Discretionary Access Control List (DACL): Specifies which users and groups have or do not have access to an object.
System Access Control List (SACL): Governs the auditing of access attempts to an object.
The process of accessing a file involves the system checking the object's security descriptor against the user's access token to determine if access should be granted and the extent of that access, based on the ACEs.
Key Components
DACL: Contains ACEs that grant or deny access permissions to users and groups for an object. It's essentially the main ACL that dictates access rights.
SACL: Used for auditing access to objects, where ACEs define the types of access to be logged in the Security Event Log. This can be invaluable for detecting unauthorized access attempts or troubleshooting access issues.
System Interaction with ACLs
Each user session is associated with an access token that contains security information relevant to that session, including user, group identities, and privileges. This token also includes a logon SID that uniquely identifies the session.
The Local Security Authority (LSASS) processes access requests to objects by examining the DACL for ACEs that match the security principal attempting access. Access is immediately granted if no relevant ACEs are found. Otherwise, LSASS compares the ACEs against the security principal's SID in the access token to determine access eligibility.
Summarized Process
ACLs: Define access permissions through DACLs and audit rules through SACLs.
Access Token: Contains user, group, and privilege information for a session.
Access Decision: Made by comparing DACL ACEs with the access token; SACLs are used for auditing.
ACEs
There arey three main types of Access Control Entries (ACEs):
Access Denied ACE: This ACE explicitly denies access to an object for specified users or groups (in a DACL).
Access Allowed ACE: This ACE explicitly grants access to an object for specified users or groups (in a DACL).
System Audit ACE: Positioned within a System Access Control List (SACL), this ACE is responsible for generating audit logs upon access attempts to an object by users or groups. It documents whether access was allowed or denied and the nature of the access.
Each ACE has four critical components:
The Security Identifier (SID) of the user or group (or their principal name in a graphical representation).
A flag that identifies the ACE type (access denied, allowed, or system audit).
Inheritance flags that determine if child objects can inherit the ACE from their parent.
An access mask, a 32-bit value specifying the object's granted rights.
Access determination is conducted by sequentially examining each ACE until:
An Access-Denied ACE explicitly denies the requested rights to a trustee identified in the access token.
Access-Allowed ACE(s) explicitly grant all requested rights to a trustee in the access token.
Upon checking all ACEs, if any requested right has not been explicitly allowed, access is implicitly denied.
Order of ACEs
The way ACEs (rules that say who can or cannot access something) are put in a list called DACL is very important. This is because once the system gives or denies access based on these rules, it stops looking at the rest.
There is a best way to organize these ACEs, and it is called "canonical order." This method helps make sure everything works smoothly and fairly. Here is how it goes for systems like Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003:
First, put all the rules that are made specifically for this item before the ones that come from somewhere else, like a parent folder.
In those specific rules, put the ones that say "no" (deny) before the ones that say "yes" (allow).
For the rules that come from somewhere else, start with the ones from the closest source, like the parent, and then go back from there. Again, put "no" before "yes."
This setup helps in two big ways:
It makes sure that if there is a specific "no," it is respected, no matter what other "yes" rules are there.
It lets the owner of an item have the final say on who gets in, before any rules from parent folders or further back come into play.
By doing things this way, the owner of a file or folder can be very precise about who gets access, making sure the right people can get in and the wrong ones can't.
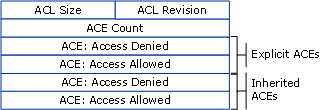
So, this "canonical order" is all about making sure the access rules are clear and work well, putting specific rules first and organizing everything in a smart way.

Use Trickest to easily build and automate workflows powered by the world's most advanced community tools. Get Access Today:
GUI Example
This is the classic security tab of a folder showing the ACL, DACL and ACEs:

If we click the Advanced button we will get more options like inheritance:

And if you add or edit a Security Principal:

And last we have the SACL in the Auditing tab:

Explaining Access Control in a Simplified Manner
When managing access to resources, like a folder, we use lists and rules known as Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Access Control Entries (ACEs). These define who can or cannot access certain data.
Denying Access to a Specific Group
Imagine you have a folder named Cost, and you want everyone to access it except for a marketing team. By setting up the rules correctly, we can ensure that the marketing team is explicitly denied access before allowing everyone else. This is done by placing the rule to deny access to the marketing team before the rule that allows access to everyone.
Allowing Access to a Specific Member of a Denied Group
Let's say Bob, the marketing director, needs access to the Cost folder, even though the marketing team generally shouldn't have access. We can add a specific rule (ACE) for Bob that grants him access, and place it before the rule that denies access to the marketing team. This way, Bob gets access despite the general restriction on his team.
Understanding Access Control Entries
ACEs are the individual rules in an ACL. They identify users or groups, specify what access is allowed or denied, and determine how these rules apply to sub-items (inheritance). There are two main types of ACEs:
Generic ACEs: These apply broadly, affecting either all types of objects or distinguishing only between containers (like folders) and non-containers (like files). For example, a rule that allows users to see the contents of a folder but not to access the files within it.
Object-Specific ACEs: These provide more precise control, allowing rules to be set for specific types of objects or even individual properties within an object. For instance, in a directory of users, a rule might allow a user to update their phone number but not their login hours.
Each ACE contains important information like who the rule applies to (using a Security Identifier or SID), what the rule allows or denies (using an access mask), and how it's inherited by other objects.
Key Differences Between ACE Types
Generic ACEs are suitable for simple access control scenarios, where the same rule applies to all aspects of an object or to all objects within a container.
Object-Specific ACEs are used for more complex scenarios, especially in environments like Active Directory, where you might need to control access to specific properties of an object differently.
In summary, ACLs and ACEs help define precise access controls, ensuring that only the right individuals or groups have access to sensitive information or resources, with the ability to tailor access rights down to the level of individual properties or object types.
Access Control Entry Layout
Type
Flag that indicates the type of ACE. Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 support six types of ACE: Three generic ACE types that are attached to all securable objects. Three object-specific ACE types that can occur for Active Directory objects.
Flags
Set of bit flags that control inheritance and auditing.
Size
Number of bytes of memory that are allocated for the ACE.
Access mask
32-bit value whose bits correspond to access rights for the object. Bits can be set either on or off, but the setting's meaning depends on the ACE type. For example, if the bit that corresponds to the right to read permissions is turned on, and the ACE type is Deny, the ACE denies the right to read the object's permissions. If the same bit is set on but the ACE type is Allow, the ACE grants the right to read the object's permissions. More details of the Access mask appear in the next table.
SID
Identifies a user or group whose access is controlled or monitored by this ACE.
Access Mask Layout
0 - 15
Object Specific Access Rights
Read data, Execute, Append data
16 - 22
Standard Access Rights
Delete, Write ACL, Write Owner
23
Can access security ACL
24 - 27
Reserved
28
Generic ALL (Read, Write, Execute)
Everything below
29
Generic Execute
All things necessary to execute a program
30
Generic Write
All things necessary to write to a file
31
Generic Read
All things necessary to read a file
References
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE) Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
Check the subscription plans!
Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.

Use Trickest to easily build and automate workflows powered by the world's most advanced community tools. Get Access Today:
Last updated